How is your retail business performing? Are you tracking the right metrics to identify growth areas and those needing improvement? Analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial for understanding your business’s health. This article outlines 25 essential retail KPIs, categorized for clarity, to help you effectively monitor and optimize your operations.
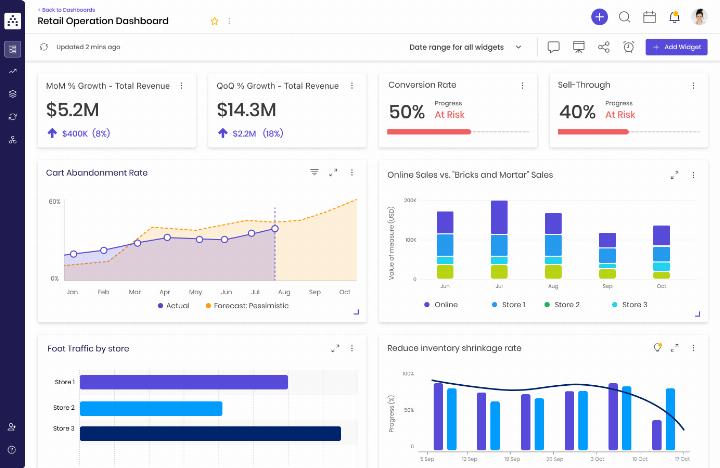 Retail KPIs dashboard in Cascade
Retail KPIs dashboard in Cascade
Retail KPI Categories
Retail KPIs can be grouped into several categories, each providing insights into different aspects of the business:
Sales Metrics: Understanding Revenue Drivers
Sales are fundamental to revenue generation. Tracking these KPIs helps understand sales performance across various channels:
- Sales Per Square Foot: Measures revenue efficiency relative to retail space. Calculate it by dividing net sales by sales space. This KPI helps assess merchandising strategies and space utilization.
- Sales Per Employee: Tracks employee performance and revenue generated per staff member. Calculate it by dividing net revenue by the number of employees. This informs decisions on training, compensation, and hiring.
- Conversion Rate: Measures the percentage of visitors who make a purchase. Divide the total transactions by the number of visitors. This reveals the effectiveness of your sales process.
Tracking sales metrics reveals revenue flow and enables informed business decisions.
Customer Behavior: Analyzing Customer Actions and Satisfaction
Understanding customer behavior is crucial for retail success. These KPIs provide insights:
- Foot Traffic: Measures the number of people entering your store. This helps assess the success of locations, ad campaigns, and product displays. Various methods exist for tracking foot traffic.
- Customer Retention Rate: Tracks the percentage of customers who return for repeat purchases. Calculate by dividing the number of customers at the end of a period by the number at the start (excluding new customers), then multiply by 100. This highlights customer loyalty and informs retention strategies.
- Customer Satisfaction: Assesses customer happiness with service and product quality. Metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and surveys gauge satisfaction. Website analytics, such as bounce rates and dwell times, provide additional insights.
- Product Return Rate: Calculates the percentage of sold items returned. A high return rate may indicate issues with product quality, fit, or customer expectations.
- Average Sales per Customer Visit: Tracks the average transaction value during each visit. Increasing this metric involves strategic store layout, product placement, and personalized recommendations.
- Cross-Selling and Upselling Rates: Measures the success of suggesting complementary or higher-value products. Effective training, product bundling, and data-driven suggestions can improve these rates.
Inventory Performance: Optimizing Stock Management
Inventory management is crucial for retail businesses. These KPIs monitor stock levels and efficiency:
- Inventory Turnover: Measures how quickly inventory is sold and replenished. Calculate it by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory. A low turnover indicates potential overstocking or deadstock.
- Average Inventory Holding Period: Calculates how long products remain in stock. Divide average inventory value by COGS and multiply by 365. Reducing this period optimizes resource allocation and cash flow.
- Gross Margin Return on Investment (GMROI): Assesses the profitability of inventory. Calculate it by dividing gross profit by average inventory cost. This identifies profitable product categories.
- Sell-Through: Measures the percentage of inventory sold compared to the initial purchase. Divide the number of units sold by the starting inventory and multiply by 100. This indicates product performance.
- Shrinkage: Calculates the percentage of inventory lost due to theft, damage, or errors. Divide inventory losses by the expected inventory. High shrinkage significantly impacts profitability.
- Stockout Rate: Measures how often a product is unavailable when a customer wants to purchase it. Divide the number of stockouts by the total number of opportunities a product should have been available and multiply by 100.
Growth Performance: Tracking Business Expansion
Monitoring growth helps identify areas for improvement and resource allocation:
- Online Sales vs. “Bricks and Mortar” Sales: Compares the performance of online and offline sales channels. This helps optimize resource allocation and marketing strategies.
- Online to Real-Life Traffic and Conversion: Tracks how online marketing drives offline store traffic. This is crucial for local SEO campaigns and optimizing online efforts.
- Year Over Year Growth: Compares the current year’s performance to the previous year’s. This reveals growth trends and identifies potential issues.
- Return on Assets (ROA): Measures how effectively assets generate profit. Divide net profit by average total assets and multiply by 100. Improving ROA indicates efficient resource utilization.
Transactional Data: Analyzing Financial Performance
These KPIs provide insights into profitability and financial health:
- Gross and Net Profit: Gross profit measures earnings after deducting production and sales costs. Net profit measures earnings after all expenses. These metrics inform cost-cutting strategies and business planning.
- Average Transaction Value: Calculates the average amount spent per customer transaction. This informs pricing and product strategies.
- Time to Fulfillment: Measures the time between order placement and shipment. Optimizing order processing and logistics reduces fulfillment time and improves customer satisfaction.
eCommerce KPIs: Measuring Online Performance
For businesses with an online presence, these KPIs are essential:
- Cost per Acquisition (CPA): Calculates the marketing cost to acquire a new customer.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: Measures the percentage of customers who abandon their shopping carts before completing a purchase.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Estimates the total revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the business.
Conclusion
Tracking these retail KPIs provides a comprehensive understanding of your business performance. By regularly monitoring and analyzing these metrics, you can make data-driven decisions to optimize operations, improve customer satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth. Utilizing a platform like Cascade can streamline KPI tracking and facilitate data-driven decision making.

