📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
IKEA, a name synonymous with affordable and stylish furniture, has dominated the global market for decades. This in-depth SWOT analysis delves into the intricate dynamics that have shaped IKEA’s journey, exploring its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. From its innovative flat-pack concept to its global presence, we’ll uncover the factors that contribute to its continued success and the challenges it faces in the ever-evolving furniture landscape.
Introduction: The IKEA Phenomenon
From its humble beginnings in Sweden, IKEA has transformed into a global furniture behemoth. With hundreds of stores spanning numerous countries, IKEA has revolutionized the way people furnish their homes. Its unique approach, combining affordability, style, and a do-it-yourself (DIY) assembly model, has resonated with consumers worldwide. This SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the internal and external factors influencing IKEA’s strategic decision-making, examining how the company leverages its strengths, addresses its weaknesses, capitalizes on opportunities, and mitigates threats.

IKEA’s Strengths: A Foundation Built on Value and Innovation
IKEA’s core strength lies in its unwavering commitment to providing value to customers, regardless of market fluctuations. This customer-centric approach is reflected in its clear vision, well-defined strategy, and innovative retail model. The simplicity of the DIY concept, allowing customers to assemble their own furniture, results in significant cost savings, which are passed on to the consumer. This focus on cost leadership has propelled IKEA to the forefront of the global furniture market.
Further bolstering its position are IKEA’s sustainable practices. The company’s emphasis on using recycled materials, optimizing resource utilization, and forging long-term supplier relationships contributes to both cost efficiency and environmental responsibility. These initiatives resonate with environmentally conscious consumers and enhance IKEA’s brand image. The vast selection of designs, catering to diverse tastes and budgets, combined with convenient delivery options, further solidifies IKEA’s appeal and strengthens its market position.
IKEA’s Weaknesses: Navigating the Challenges of Global Scale
Operating on a global scale presents inherent challenges. Maintaining consistent quality across numerous locations and product lines can be a significant hurdle. While IKEA strives for uniformity, ensuring reproducible and scalable quality assurance remains a key weakness. The relentless pursuit of cost leadership can sometimes compromise quality, particularly in the face of rising raw material prices. This balancing act between affordability and quality requires constant attention.
Another area of concern is customer feedback regarding product durability. Reports of furniture failing shortly after assembly highlight the need for continuous improvement in quality control and product design. Furthermore, effectively communicating IKEA’s environmental policies to stakeholders requires ongoing effort and transparency.
IKEA’s Opportunities: Embracing Sustainability and Expanding Reach
The growing trend of ethical consumerism presents a significant opportunity for IKEA. Consumers are increasingly drawn to environmentally responsible products, and IKEA’s “green” marketing strategy positions the company to capitalize on this trend. By showcasing its commitment to sustainability, IKEA can attract a growing segment of eco-conscious customers.
IKEA’s established market presence provides a strong foundation for further expansion. The company’s deep understanding of the furniture industry, combined with its cost leadership strategy, positions it well to enter new markets and capture untapped customer bases, particularly in developing countries like China and India. The rise of e-commerce also presents an opportunity to expand online operations and reach a wider audience.
IKEA’s Threats: Competition and Changing Consumer Dynamics
The competitive landscape of the furniture industry is constantly evolving. Competitors have emulated IKEA’s low-cost, DIY model, requiring the company to continuously innovate to maintain its competitive edge. The emergence of online retailers, often operating with lower overhead costs, poses a significant challenge. IKEA must adapt to these evolving market dynamics to retain its market share.
Internal challenges, such as employee dissatisfaction and potential legal issues, also pose a threat. Addressing these concerns is crucial for maintaining a positive brand image and avoiding costly legal battles. Furthermore, declining new customer acquisition rates necessitate a proactive approach to attracting new customers and retaining existing ones.
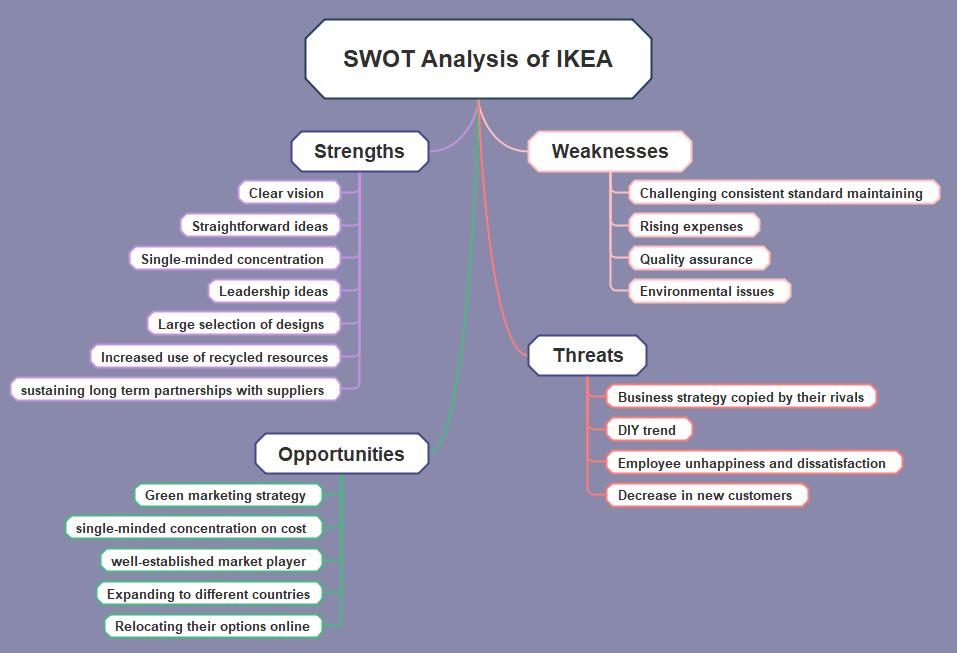
Mind Map: Visualizing IKEA’s Strategic Landscape
This mind map provides a visual representation of IKEA’s SWOT analysis, highlighting the key factors influencing the company’s strategic direction. It captures the essence of IKEA’s business model, its focus on cost leadership through the DIY concept, and its global reach through both online and offline operations.
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about IKEA’s SWOT Analysis
Q: How does IKEA’s flat-pack concept contribute to its cost leadership strategy?
A: The flat-pack design reduces shipping and storage costs, allowing IKEA to offer lower prices to consumers. It also empowers customers to participate in the assembly process, further reducing costs.
Q: What are some of the challenges IKEA faces in maintaining consistent quality across its global operations?
A: Managing a vast network of suppliers and manufacturing facilities across different countries can make it difficult to ensure consistent quality control. Variations in materials, labor practices, and manufacturing processes can lead to inconsistencies in the final product.
Q: How can IKEA capitalize on the growing trend of sustainable consumerism?
A: IKEA can highlight its commitment to using recycled materials, reducing waste, and implementing environmentally friendly practices in its operations. Communicating these efforts transparently to consumers can attract environmentally conscious buyers.
Q: What are some of the competitive threats IKEA faces in the online retail space?
A: Online retailers often have lower overhead costs than traditional brick-and-mortar stores, allowing them to offer competitive prices. IKEA needs to strengthen its online presence and offer a seamless online shopping experience to compete effectively.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below. Let’s discuss the future of IKEA and its position in the global furniture market.
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download