The restaurant industry faced unprecedented challenges in 2020, incurring losses exceeding $240 billion in the US alone. Disrupted supply chains and drastically altered consumer habits forced businesses to rethink their strategies. Amidst this turmoil, a new business model emerged, poised to revolutionize the fast-food landscape: the Virtual Dining Concept (VDC). This article delves into the innovative approach of VDC, the driving force behind MrBeast Burgers, and explores why established fast-food giants failed to capitalize on this disruptive concept.
MrBeast Burgers: A Case Study in Disruptive Innovation
In December 2020, YouTuber Jimmy Donaldson, better known as MrBeast, launched MrBeast Burgers, opening an astonishing 300 locations virtually overnight. This rapid expansion occurred during a period when many restaurants struggled to survive, highlighting the disruptive potential of the VDC model. To put this growth into perspective, McDonald’s took six years to reach the same number of franchise locations.
 MrBeast Burger locations across the US
MrBeast Burger locations across the US
The COVID-19 pandemic and its associated restrictions left many restaurant kitchens underutilized. VDC capitalized on this idle capacity by partnering with existing restaurants to produce and package MrBeast Burgers. Leveraging popular delivery apps like UberEats, DoorDash, and Postmates, VDC created a streamlined delivery system, effectively transforming traditional restaurants into virtual kitchens.
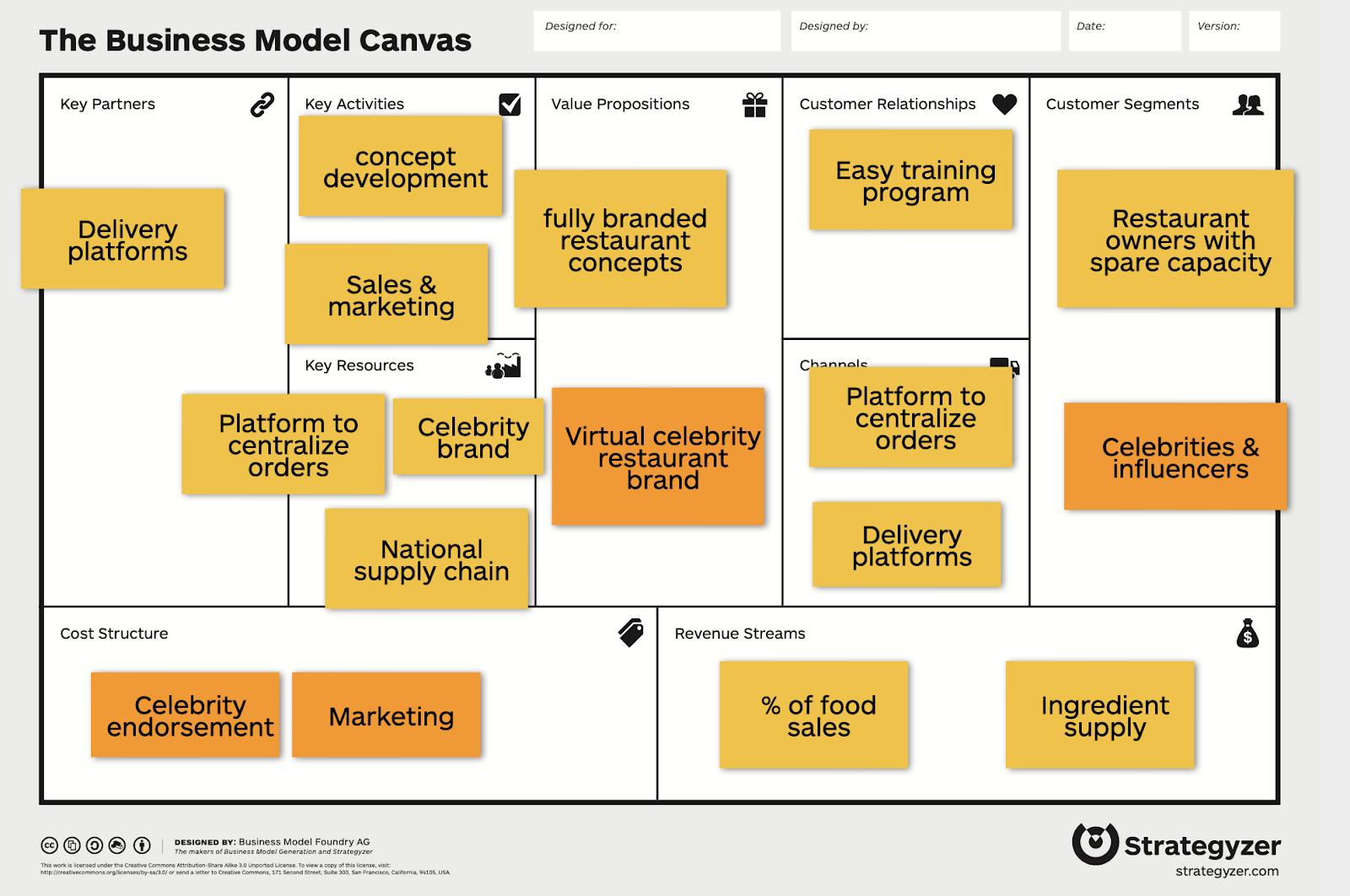 Virtual Dining Concept business model
Virtual Dining Concept business model
The Power of Virtual Dining Concepts: Beyond MrBeast
MrBeast Burgers represents just one facet of VDC’s broader strategy. The brainchild of restaurateur Robert Earl, VDC partners with numerous celebrities to create virtual restaurant brands. These “ghost kitchens” operate within existing restaurants, utilizing their existing infrastructure and staff to prepare and fulfill orders exclusively through delivery platforms.
VDC provides partner restaurants with ingredients, branding, and a centralized app to manage orders from various delivery services. In exchange, restaurants receive 30% of the profits. This model offers a compelling value proposition: increased revenue without significant investment, achieved through more efficient resource utilization.
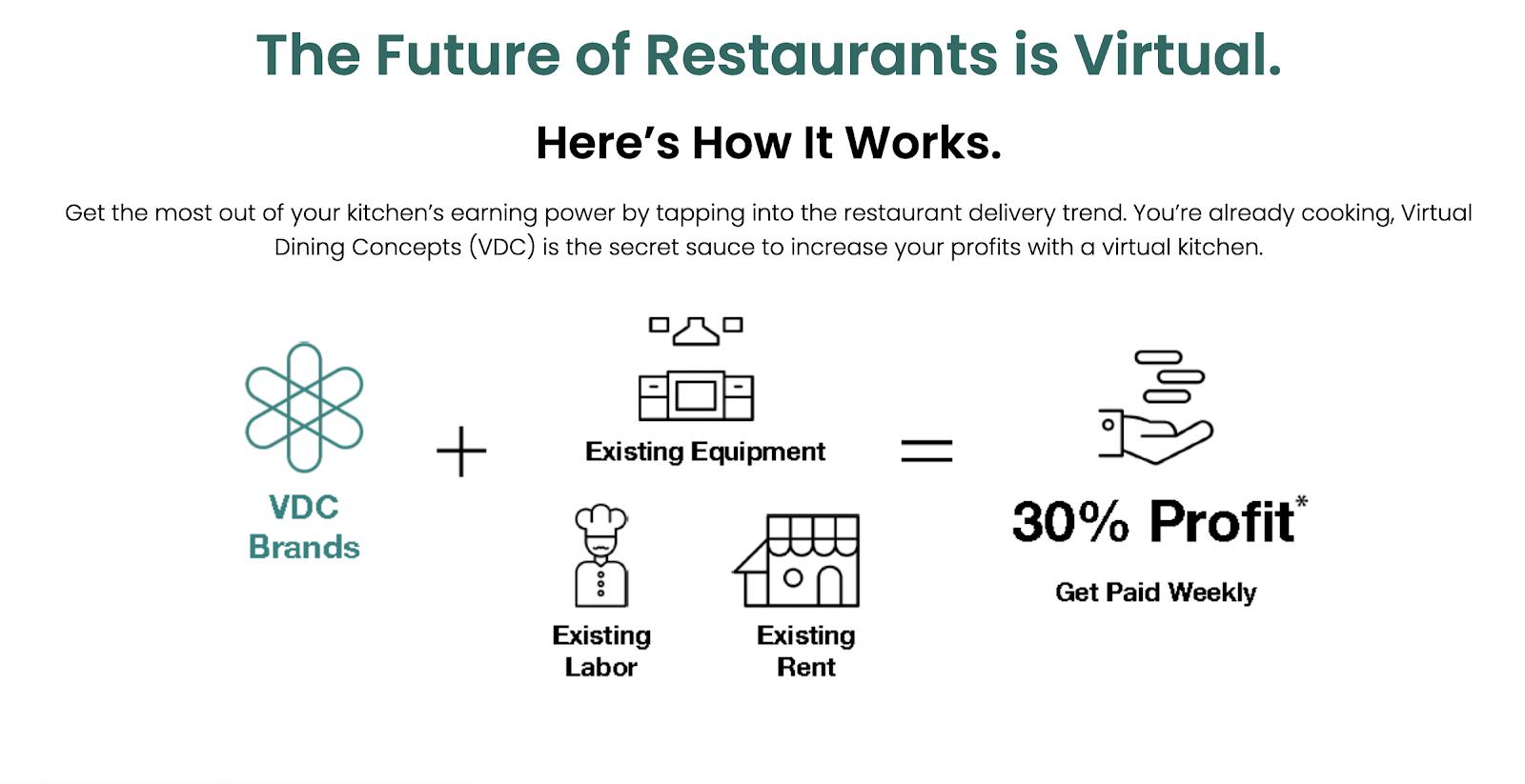 Virtual Dining Concept benefits for restaurants
Virtual Dining Concept benefits for restaurants
Leveraging Celebrity Influence and Delivery Algorithms
VDC strategically leverages the star power of celebrities to generate buzz and attract customers. From Mariah Carey’s Cookies to Tyga’s Chicken Bites, VDC capitalizes on existing fan bases to promote its virtual brands. The celebrities endorse and market the products, while VDC focuses on developing the food concepts and managing the operational aspects.
Furthermore, VDC utilizes the algorithms of food delivery apps to maximize reach and optimize delivery efficiency. Traditional restaurants are often limited by their geographical proximity to customers. However, by partnering with restaurants strategically located throughout a city, VDC ensures wider coverage and accessibility for customers across the entire urban area, overcoming the typical five-mile radius limitation of many delivery apps.
The Incumbent’s Dilemma: Why Established Chains Missed the Mark
The question remains: why didn’t established fast-food giants like McDonald’s or Burger King pioneer this disruptive model? These companies possess extensive resources, established delivery systems, and global brand recognition. The answer lies in the inherent inertia of successful businesses. Incumbent organizations are often locked into existing, profitable business models. Their structures and processes are optimized for these models, leading to resistance against radical innovation. This “corporate antibody” syndrome can stifle creativity and prevent companies from adapting to evolving market dynamics.
Building an Exploration Engine: The Key to Combating Disruption
To combat this inertia, established companies must cultivate a culture of exploration and innovation. They need to create dedicated “exploration engines” – structures that empower experimentation and enable the development of radically new business models. By leveraging their existing strengths and assets, incumbents can proactively address disruption and compete effectively against agile, innovative newcomers. The VDC model demonstrates the power of reimagining existing resources and embracing new technologies to create disruptive value in a rapidly changing market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Virtual Dining Concept (VDC)? A VDC is a business model that utilizes existing restaurant kitchens to create delivery-only restaurant brands. These “ghost kitchens” operate without a physical storefront and rely on third-party delivery apps for order fulfillment.
How does the VDC model benefit restaurants? It allows restaurants to increase revenue by utilizing idle kitchen capacity, without requiring significant capital investment.
Why are celebrity partnerships important for VDCs? Celebrities provide brand recognition and marketing power, attracting customers and generating buzz for the virtual restaurant brands.
How do VDCs overcome the geographical limitations of delivery apps? By partnering with multiple restaurants across a city, VDCs can ensure broader delivery coverage and reach a wider customer base.
We encourage you to share this article and contribute to the conversation. What are your thoughts on the future of the restaurant industry and the role of virtual dining concepts? Let us know in the comments below!

