📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
PESTEL analysis is a strategic framework used to identify and analyze macro-environmental factors that can significantly impact a business’s operations and performance. This framework examines Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors, providing a holistic view of the external landscape. Understanding these influences is crucial for developing effective strategies, mitigating risks, and capitalizing on opportunities.
 A woman analyzing market trends, representing the concept of PESTEL analysis
A woman analyzing market trends, representing the concept of PESTEL analysis
This article will delve into each element of the PESTEL framework, providing examples and demonstrating how businesses can leverage this powerful tool for strategic decision-making.
Political Factors
Political factors encompass government policies, regulations, and political stability. These factors can influence market access, trade tariffs, tax rates, and overall business confidence. Examples include:
- Trade Policies: Changes in international trade agreements can impact import/export costs and market access.
- Political Stability: A volatile political environment can deter investment and disrupt business operations.
- Taxation: Corporate tax rates and tax incentives can significantly affect profitability.
Economic Factors
Economic factors relate to the overall economic climate, including growth rates, inflation, interest rates, and unemployment. These factors can impact consumer spending, investment decisions, and overall business performance. Examples include:
- Economic Growth: A strong economy can boost consumer confidence and drive business expansion.
- Inflation: Rising inflation can erode purchasing power and increase input costs.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can affect borrowing costs and investment decisions.
 A graph depicting economic trends and data relevant to PESTEL analysis
A graph depicting economic trends and data relevant to PESTEL analysis
Social Factors
Social factors reflect societal trends, cultural norms, values, and demographics. Understanding these factors can help businesses tailor their products and marketing strategies to effectively reach target audiences. Examples include:
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
- Demographics: Changes in population age, ethnicity, and income levels can influence consumer preferences.
- Cultural Trends: Shifting social values and lifestyles can create new market opportunities.
- Consumer Behavior: Understanding consumer buying habits and preferences is crucial for product development and marketing.
Technological Factors
Technological factors encompass advancements in technology, automation, research and development, and the rate of technological change. These factors can create new industries, disrupt existing ones, and influence production processes and efficiency. Examples include:
- Automation: Automation can improve productivity and reduce labor costs, but may also lead to job displacement.
- Innovation: Technological innovations can create new products and services, revolutionizing industries.
- R&D Investment: Investment in research and development can drive technological advancements and competitive advantage.
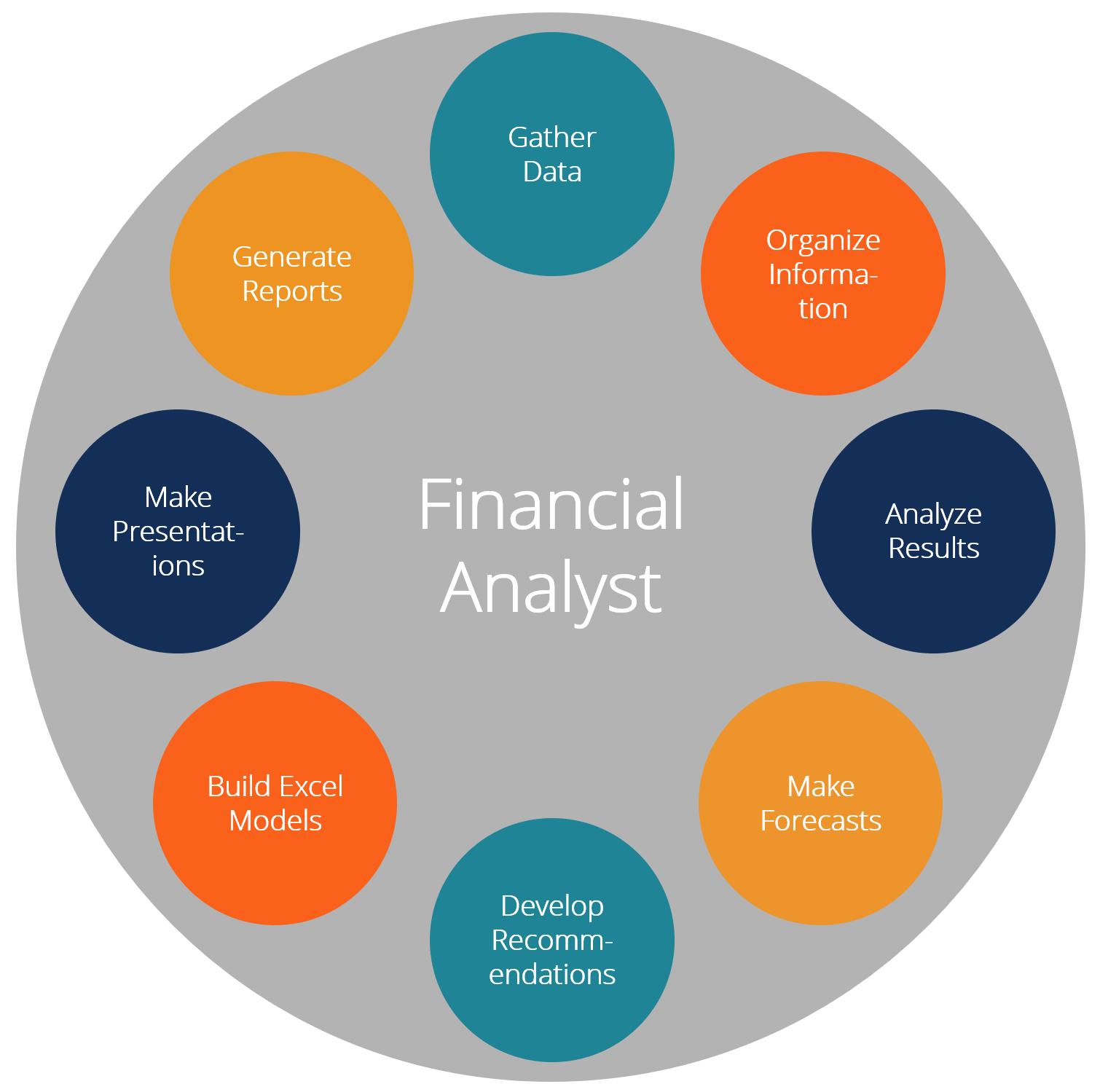
 An image representing financial modeling and its relevance to analyzing technological factors in PESTEL
An image representing financial modeling and its relevance to analyzing technological factors in PESTEL
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors involve ecological and environmental concerns, including climate change, pollution, resource scarcity, and sustainability practices. These factors are becoming increasingly important for businesses, impacting their reputation, operations, and long-term viability. Examples include:
- Climate Change: Businesses need to adapt to changing weather patterns and mitigate their environmental impact.
- Sustainability: Consumers are increasingly demanding environmentally friendly products and practices.
- Resource Scarcity: Limited access to natural resources can impact production costs and supply chains.
Legal Factors
Legal factors involve laws and regulations that businesses must comply with, including labor laws, consumer protection laws, and antitrust regulations. These factors can impact business operations, costs, and legal liabilities. Examples include:
- Labor Laws: Compliance with minimum wage laws and worker safety regulations can affect labor costs.
- Consumer Protection: Businesses must adhere to consumer protection laws regarding product safety and advertising.
- Antitrust Laws: Regulations aimed at preventing monopolies and promoting fair competition can impact market dynamics.
Conclusion
PESTEL analysis is a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes to understand the external environment and develop strategies that align with market realities. By systematically analyzing Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors, businesses can proactively address challenges, seize opportunities, and build a sustainable competitive advantage. Conducting regular PESTEL analyses can help businesses stay ahead of the curve and navigate the complexities of the ever-evolving business landscape.
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are
FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human. Read More & Download

