📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
Human Resource Management (HRM) is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Understanding the core functions of HR is the first step to building a successful organization. This article explores the seven HR basics, providing a comprehensive overview of the essential elements of effective HRM. We’ll delve into each function, exploring its importance and how it contributes to overall organizational success. We’ll also touch on the evolution of HRM and the essential skills required for modern HR professionals.
Introduction to Human Resource Management
HRM is a strategic approach to managing employees, designed to enhance organizational performance. It encompasses attracting, managing, and retaining employees who contribute to the company’s success. Effective HRM ensures employees are aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and culture. Functions like recruitment, compensation, and employee development are all key components of a comprehensive HRM strategy. For example, hiring individuals who resonate with your company culture can lead to increased happiness, retention, and productivity. Similarly, engaged employees deliver higher quality work and improve customer satisfaction, demonstrating the tangible benefits of effective HRM.
 Five ways how HR Management contributes to organizational success.
Five ways how HR Management contributes to organizational success.
The 7 Cornerstones of HRM
Effective HRM relies on seven core elements:
- Recruitment & Selection
- Performance Management
- Learning & Development
- Succession Planning
- Compensation and Benefits
- Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS)
- HR Data and Analytics
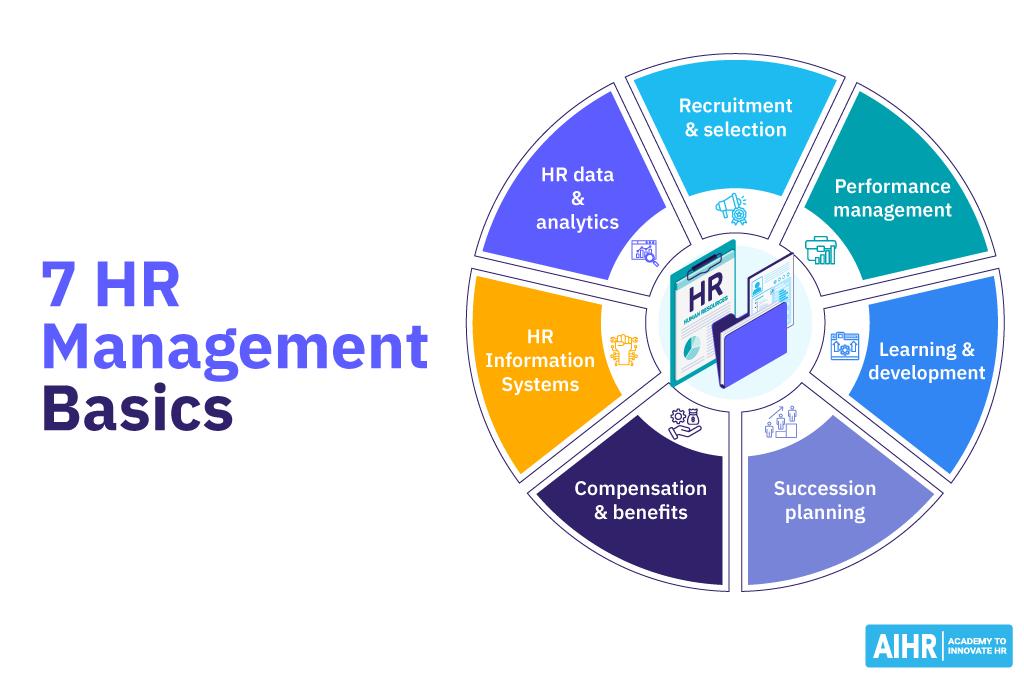 7 HR Management basics include recruitment, succession planning, and five other cornerstones.
7 HR Management basics include recruitment, succession planning, and five other cornerstones.
1. Recruitment & Selection
This process aims to attract and hire the best candidates for open positions. Recruitment focuses on attracting potential applicants, while selection involves evaluating and choosing the most suitable candidate. The process includes defining job requirements, advertising vacancies, sourcing candidates, screening resumes, conducting interviews, and finally, extending job offers.
2. Performance Management
Performance management is a continuous process designed to enhance employee performance. It involves setting clear expectations, establishing individual goals aligned with organizational objectives, providing regular feedback, conducting performance reviews, and evaluating results. Effective performance management systems contribute to a productive and positive work environment.
3. Learning & Development (L&D)
L&D is a systematic process that improves employee skills, knowledge, and competencies. Learning focuses on acquiring new skills and knowledge, while development aims to broaden existing capabilities and prepare employees for future roles. L&D programs can include training sessions, workshops, mentoring programs, and online courses.
4. Succession Planning
Succession planning involves preparing for the departure of key employees by identifying and developing internal candidates to fill critical roles. This ensures business continuity and minimizes disruption caused by employee turnover. Succession planning focuses on critical roles, key talent, and maintaining continuity within the organization.
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
5. Compensation and Benefits
This involves designing and administering a competitive compensation and benefits package to attract and retain top talent. This includes salary, bonuses, insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. A well-structured compensation and benefits program is crucial for employee motivation and satisfaction.
6. Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS)
HRIS are digital systems that support various HR functions, including recruitment, performance management, and payroll. These systems streamline HR processes, improve efficiency, and provide valuable data for decision-making.
7. HR Data and Analytics
HR data and analytics involve collecting, analyzing, and interpreting HR data to gain insights into workforce trends and make informed decisions. This includes using HR metrics and KPIs to track performance, identify areas for improvement, and develop data-driven HR strategies.
The Evolution of HRM
HRM has significantly evolved over time. Initially focused on employee well-being and productivity, HRM has transitioned to a strategic function aligned with organizational goals. Today, HR professionals are expected to be strategic partners, driving organizational success through effective people management. Future HR trends point towards an increased focus on adapting to workforce changes and redefining the relationship between talent and employers.

Essential Skills for HR Professionals
Modern HR professionals require a diverse skill set:
- HR-Specific Skills: HRM knowledge, administrative expertise, employee experience management.
- Business Acumen: Commercial awareness, HR strategy development, advisory skills.
- Soft Skills: Communication, active listening, proactivity.
- Digital & Data Literacy: HR reporting, analytical skills, technology proficiency.
Conclusion
These seven HR basics are interconnected and essential for building a high-performing workforce. Each element contributes to the overall strength of the HR function, enabling organizations to achieve their strategic objectives. By understanding and effectively managing these core components, businesses can create a positive and productive work environment that attracts, retains, and develops top talent.
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download

