📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
As businesses navigate the rapidly evolving digital landscape of 2025, optimizing business processes has become more critical than ever. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of business processes, offering valuable insights for business technology partners, IT leaders, and anyone seeking to enhance organizational efficiency and drive growth. From defining a business process to leveraging cutting-edge technology, this guide provides a roadmap for streamlining operations and achieving strategic objectives.

The dynamic interplay between technology and process optimization is transforming the way businesses operate. This guide serves as a strategic toolkit, empowering leaders to overcome challenges like legacy systems and agile development. By orchestrating streamlined processes, organizations can cultivate a culture of efficiency, innovation, and excellence in 2025 and beyond. This guide aims to demystify the concept of business processes, providing a clear understanding of their importance and practical application.
Understanding Business Processes: Definition and Significance
A business process is a series of interconnected tasks or activities performed by individuals or systems to achieve a specific organizational goal. These processes are structured and designed to deliver a pre-defined outcome, contributing directly to business success and growth. Think of it as a set of coordinated actions that, when executed correctly, lead to a desired result.
Why Business Processes Matter
Well-defined business processes are crucial for organizations of all sizes, especially large enterprises. They form the backbone of efficient operations, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively and that activities align with overall business objectives.
 the_importance_of_business_processes
the_importance_of_business_processes
Key Benefits of Well-Defined Business Processes:
- Focus on Strategic Goals: Clearly defined processes highlight tasks that directly contribute to achieving larger business objectives.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined processes eliminate redundancies and bottlenecks, leading to improved productivity.
- Improved Communication: Well-defined processes facilitate seamless communication between teams, departments, and stakeholders.
- Accountability and Resource Optimization: Established approval workflows ensure accountability and optimal use of resources.
- Operational Stability: Processes prevent chaos and maintain consistency in day-to-day operations.
- Standardization: Standardized procedures ensure consistency and quality in task completion.
Types of Business Processes
Business processes can be categorized into three main types:
1. Operational Processes
These core processes directly generate value for customers and the organization. They are essential for revenue generation and include activities like product manufacturing, order fulfillment, and service delivery.
2. Support Processes
Supporting processes enable and enhance the effectiveness of operational processes. While they don’t directly generate revenue, they are crucial for internal operations. Examples include human resources management, finance, and IT support.
3. Management Processes
These processes oversee and control both operational and support processes. They focus on planning, monitoring, and continuous improvement. Examples include strategic planning, performance management, and risk management.
Leveraging Technology for Business Process Optimization
Business process technology utilizes software and systems to automate, streamline, and optimize business processes. This technology helps organizations improve efficiency, reduce errors, and save time and resources.
Examples of business process technology include:
- Workflow Management Software: Automates and manages complex workflows.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Streamlines customer interactions and manages customer data.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: Integrates various business functions into a single system.
The Business Process Lifecycle: A 7-Step Guide
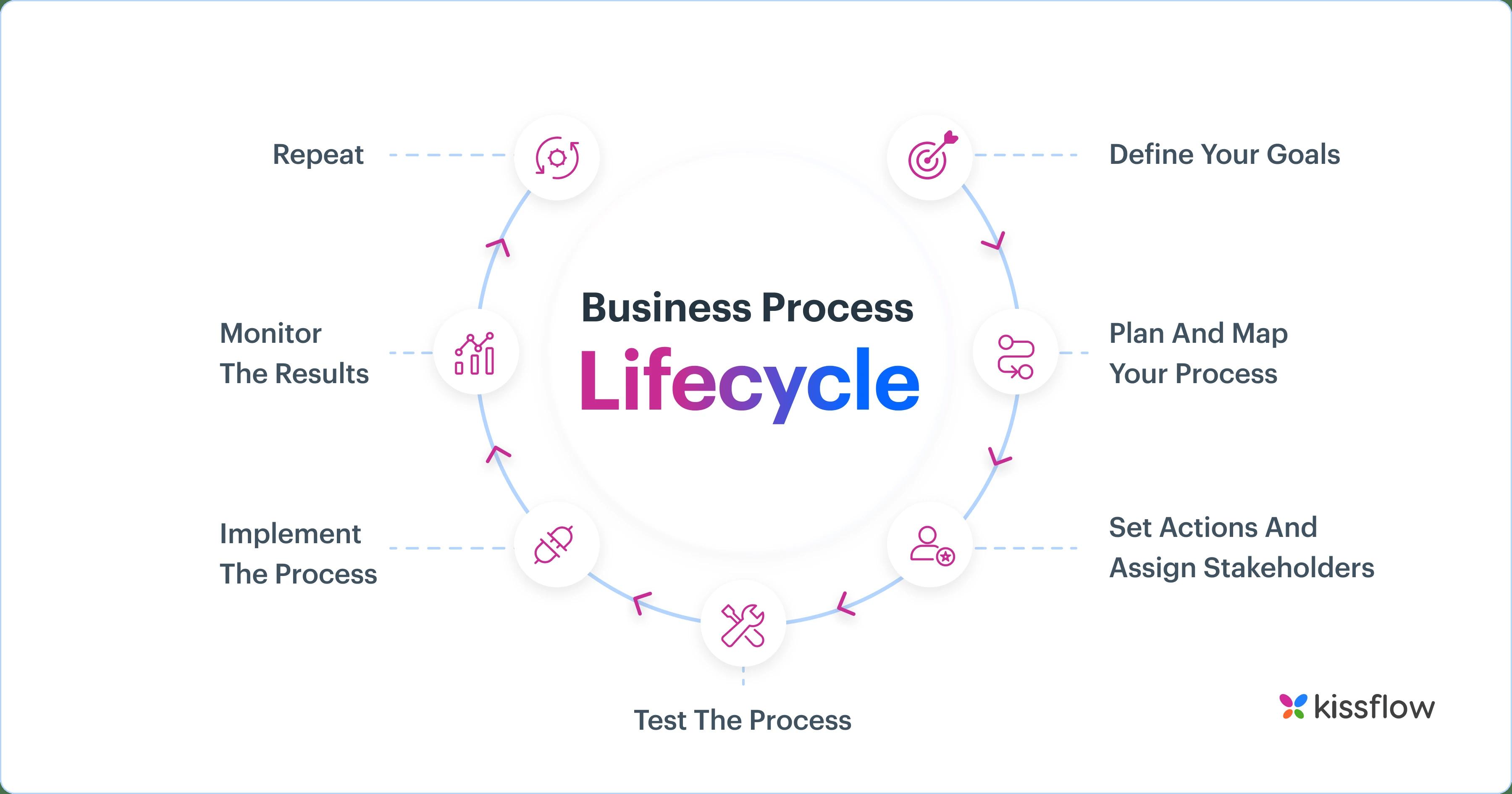 the_7_steps_of_the_business_process_lifecycle
the_7_steps_of_the_business_process_lifecycle
The business process lifecycle provides a framework for developing and managing effective processes:
- Define Goals: Clearly define the purpose and desired outcomes of the process.
- Plan and Map: Develop a detailed plan and visual representation of the process workflow.
- Assign Actions and Stakeholders: Identify specific tasks and assign responsibilities to individuals or systems.
- Test the Process: Conduct a pilot test to identify and address any gaps or inefficiencies.
- Implement the Process: Roll out the process in a live environment with proper communication and training.
- Monitor Results: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyze the process performance.
- Repeat and Improve: Continuously review and refine the process based on monitoring data and feedback.
Measuring Business Process Success
Measuring the effectiveness of business processes is crucial for continuous improvement. This involves:
- Identify KPIs: Select relevant metrics aligned with business objectives, such as time, cost, quality, and productivity.
- Collect Data: Utilize tools and software to gather data related to the identified KPIs.
- Analyze Data: Employ data analytics techniques to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
- Implement Improvements: Based on the data analysis, implement changes to optimize the process.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitor and analyze data to ensure ongoing improvement and adaptation.
Benefits of Business Process Software
 benefits_of_using_business_process_software
benefits_of_using_business_process_software
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
Implementing business process management (BPM) software offers numerous advantages:
- Risk Reduction: BPM software helps identify and mitigate potential risks and bottlenecks.
- Eliminate Redundancies: Process monitoring allows for the identification and elimination of duplicated tasks.
- Cost Minimization: Improved process visibility helps identify and reduce wasteful spending.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Transparency fostered by BPM software promotes collaboration across teams and departments.
- Increased Agility: Optimized processes enable organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Improved Productivity: Streamlined workflows and automated tasks boost team productivity.
- Higher Efficiency: Dashboards provide real-time insights into process performance, allowing for data-driven decision-making.
- Improved Compliance: BPM software facilitates compliance with industry regulations and standards.
Attributes of an Ideal Business Process
An effective business process should exhibit the following characteristics:
- Finite: A clear beginning and end, with a defined number of steps.
- Repeatable: Capable of being executed multiple times consistently.
- Value-Creating: Each step adds value and contributes to the overall goal.
- Flexible: Adaptable to changes and improvements as needed.
Related Terms and Concepts
Understanding related terminology is essential for effective business process management:
- Business Process Automation (BPA): The use of technology to automate specific tasks within a process.
- Business Process Management (BPM): A holistic approach to continuously improve and optimize business processes.
- Business Process Modeling: Visually representing a process and its workflow.
- Business Process Improvement: Analyzing and modifying existing processes to enhance efficiency.
- Business Process Re-engineering: Radically redesigning processes for dramatic improvements.
- Business Process Optimization: Fine-tuning existing processes to eliminate bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Business Process Mapping: Documenting and visualizing a process flow.
- Business Process Analysis: Identifying business requirements and designing solutions.
- Business Process Integration: Connecting different systems and processes to share information seamlessly.
- Business Process Simulation: Testing and analyzing process performance under various conditions.
- Business Process Transformation: Fundamentally changing processes to align with business goals.
- Business Process Flow: The sequence of steps and activities within a process.
- Business Process Monitoring: Tracking process performance and identifying areas for improvement.
- Business Rules Engines (BREs): Automating decision-making based on pre-defined rules.
Creating Effective Business Processes
Designing and implementing effective business processes requires a clear understanding of business goals, stakeholder involvement, and the appropriate use of technology. Modern BPM software empowers businesses to create and manage processes efficiently, driving organizational success in today’s competitive landscape.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about business processes:
Q: What is the difference between a process and a procedure?
A: A process is a high-level overview of activities, while a procedure provides detailed instructions for specific tasks within a process.
Q: How can I get started with business process improvement?
A: Start by identifying key processes, mapping their current state, analyzing their performance, and identifying areas for improvement.
Q: What are some common challenges in implementing BPM software?
A: Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of stakeholder buy-in, and data integration issues.
Q: What are the key factors to consider when choosing BPM software?
A: Consider factors such as ease of use, scalability, integration capabilities, and cost.
We encourage you to share your questions and insights in the comments below. Join the conversation and contribute to the ongoing discussion about optimizing business processes for success in 2025 and beyond!
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
