📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
Stakeholder mapping is a crucial process for any organization, particularly in today’s dynamic business environment. It allows businesses to identify, analyze, and prioritize their stakeholders based on various factors such as their influence, interest, and impact on the organization’s objectives. Effective stakeholder mapping empowers organizations to develop targeted communication and engagement strategies, fostering stronger relationships and increasing the likelihood of project success. This comprehensive guide will delve into the importance of stakeholder mapping, explore different models and approaches, and provide practical tips for creating your own stakeholder map.
 alt text: A visual representation of stakeholder mapping with different stakeholders categorized based on their influence and interest.
alt text: A visual representation of stakeholder mapping with different stakeholders categorized based on their influence and interest.
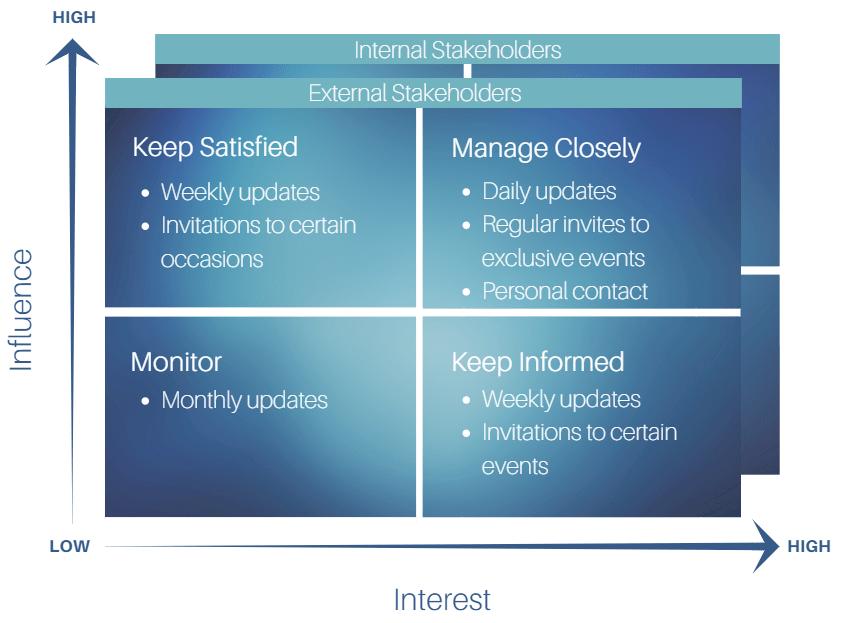
After identifying key stakeholders, organizations need to analyze their influence and interest to effectively prioritize engagement. A classic approach utilizes a matrix that plots stakeholders based on these two factors. This visual representation helps categorize stakeholders into groups such as those with high influence and high interest, requiring the most attention, versus those with low influence and low interest, who may need less frequent communication.
It’s essential to remember that stakeholder mapping is not a static process. The relationships and influence of stakeholders can shift over time, influenced by factors like market changes, social media trends, and evolving community expectations. Regularly reviewing and updating your stakeholder map ensures that your engagement strategies remain relevant and effective. A dynamic approach to stakeholder mapping enables organizations to adapt to these changes and maintain strong relationships with their key stakeholders.
Understanding the concept of operational management is crucial for effective stakeholder management. Operational management focuses on the efficient and effective execution of business operations, ensuring that processes are streamlined and aligned with organizational goals. A strong operational management framework can facilitate smoother stakeholder interactions by providing a reliable and predictable platform for communication and engagement. For a deeper understanding of operational management and its significance in business, check out our article on Explained: What is Operational Management and Why It Matters in Business?.
Traditional Stakeholder Mapping Models
Several established models provide frameworks for stakeholder mapping. One common approach involves categorizing stakeholders based on their power, legitimacy, and urgency.
The Power/Urgency/Legitimacy Model
This model, developed by Mitchell, Agle, and Wood, helps anticipate stakeholder behavior by assessing their:
- Power: The ability to influence the organization’s decisions and actions.
- Legitimacy: The validity and appropriateness of their relationship with the organization.
- Urgency: The time-sensitivity and criticality of their claims or demands.
Based on these three attributes, stakeholders are classified into different categories, such as:
- Latent Stakeholders: Possessing only one of the three characteristics (power, legitimacy, or urgency), these stakeholders are considered less critical but still require monitoring.
- Expectant Stakeholders: Exhibiting two of the three characteristics, these stakeholders have a more significant impact and require more attention. Often, they have a direct financial stake or are directly affected by the project’s outcomes.
- Definitive Stakeholders: Possessing all three characteristics, these stakeholders are considered the most crucial and demand the highest priority in engagement efforts.
While these traditional models offer a starting point, it’s important to acknowledge their limitations in today’s complex environment. For instance, a “latent” stakeholder can quickly gain influence through social media, significantly impacting a project. The accessibility of social media platforms has amplified the voices of previously less influential stakeholders, making it crucial for organizations to monitor and engage with a wider range of stakeholders than traditional models might suggest.
Modern Approaches to Stakeholder Mapping
Modern stakeholder mapping takes a more nuanced approach, considering the evolving power dynamics and expectations of stakeholders in the digital age. This involves moving beyond simple categorization and incorporating a deeper understanding of stakeholder relationships, motivations, and communication preferences.
Multi-Dimensional Stakeholder Mapping
A multi-dimensional approach goes beyond traditional grids to offer a more comprehensive view of the stakeholder landscape. This includes:
- Segmentation: Grouping stakeholders based on shared interests, functions, or demographics provides a more granular understanding of their needs and expectations.
- Connection Mapping: Visualizing the relationships between different stakeholders can reveal hidden alliances, potential conflicts, and opportunities for collaboration. Understanding these connections helps tailor communication strategies and build stronger relationships within the stakeholder network.
- Custom Fields: Tracking additional information, such as demographics, communication preferences, and past interactions, enriches the stakeholder profile and allows for more personalized engagement.
- Scalable Criteria: Assessing stakeholders on a scale for influence, interest, impact, criticality, position, and effort provides a more detailed understanding of their relative importance and potential contribution to the project.
This approach allows organizations to tailor their engagement strategies, ensuring that communication is targeted and effective for each stakeholder group. By understanding the specific needs and motivations of different stakeholders, organizations can build stronger relationships and increase the likelihood of achieving their objectives.
Utilizing a Balanced Scorecard can be incredibly valuable in aligning stakeholder expectations with business strategy. The Balanced Scorecard provides a framework for measuring performance across various perspectives, including financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. By considering these different perspectives, organizations can gain a holistic understanding of stakeholder needs and ensure that their strategies address these needs effectively. To delve deeper into the Balanced Scorecard and its application in business management, explore our comprehensive guide: What is Balanced Scorecard in Business Management? A Comprehensive Guide.
Dynamic Stakeholder Mapping: Tracking Changes Over Time
Recognizing that stakeholder dynamics are not static is essential for effective engagement. Tracking changes in stakeholder influence, interest, and position over time allows organizations to proactively adapt their strategies and maintain strong relationships. This involves regularly reviewing and updating the stakeholder map, incorporating feedback from stakeholders, and monitoring external factors that may influence their perspectives.
 alt text: A visual representation of stakeholder mapping with different stakeholders categorized based on their influence and interest.
alt text: A visual representation of stakeholder mapping with different stakeholders categorized based on their influence and interest.
Building Your Stakeholder Map: Practical Steps
Creating a stakeholder map involves a systematic approach:
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
Identify Stakeholders: Begin by brainstorming all individuals, groups, or organizations that may be affected by or have an interest in your project or organization. This can include internal stakeholders like employees and management, as well as external stakeholders such as customers, suppliers, community groups, and government agencies.
Analyze Stakeholder Attributes: Assess each stakeholder based on their influence, interest, and impact on your objectives. Use a matrix or other visual representation to categorize them based on these attributes.
Develop Engagement Strategies: Tailor your communication and engagement approach for each stakeholder group based on their level of influence and interest. High-influence, high-interest stakeholders require proactive and frequent communication, while those with lower influence and interest may need less frequent updates.
Monitor and Review: Regularly review and update your stakeholder map to reflect changes in stakeholder dynamics and ensure that your engagement strategies remain relevant and effective.
Effective stakeholder management also necessitates understanding risk management principles. Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to an organization’s objectives. By proactively addressing risks, organizations can minimize negative impacts on stakeholders and maintain their trust and confidence. To learn more about risk management and its importance in business, refer to our article on Explained: What is Risk Management and Why It Matters in Business?.
Conclusion: The Power of Effective Stakeholder Mapping
Stakeholder mapping is not merely a project management tool; it’s a strategic imperative for organizations operating in today’s complex and interconnected world. By understanding and effectively engaging with their stakeholders, organizations can build stronger relationships, manage expectations, and increase the likelihood of achieving their objectives. Embracing a dynamic and multi-dimensional approach to stakeholder mapping empowers organizations to navigate the evolving landscape of stakeholder relationships and create a sustainable path to success.
FAQs
Q: How often should I update my stakeholder map?
A: It’s recommended to review and update your stakeholder map at least quarterly, or more frequently if significant changes occur in your project or organization’s environment.
Q: What are some common challenges in stakeholder mapping?
A: Challenges can include difficulty in identifying all relevant stakeholders, accurately assessing their influence and interest, and maintaining consistent engagement over time.
Q: How can I engage with stakeholders who have conflicting interests?
A: Facilitating open communication and seeking common ground are key to managing conflicting interests. Focus on building trust and transparency to foster a collaborative environment.
We encourage you to share your own experiences and insights on stakeholder mapping. What challenges have you encountered, and what strategies have you found effective? Let us know in the comments below!
Understanding how to manage stakeholders effectively is essential for navigating the complexities of modern business. Stakeholder management involves building and maintaining positive relationships with individuals and groups who have an interest in your organization’s success. This requires effective communication, proactive engagement, and a commitment to addressing stakeholder concerns. To explore the importance of stakeholder management in business, read our article on Explained: What is Stakeholder Management and Why It Matters in Business?. Furthermore, understanding the role of change management in incorporating new stakeholder mapping strategies is crucial. Effective change management ensures a smooth transition and minimizes disruption to ongoing operations. To learn more about the role of change management in modern business, check out our article on What is the Role of Change Management in Modern Business Management?.
📚 Unlock the World of AI and Humanity with These Two Free Books! 🚀
Dive into the thrilling realms of artificial intelligence and humanity with "The ECHO Conundrum" and "Awakening: Machines Dream of Being Human". These thought-provoking novels are FREE this week! Don't miss the chance to explore stories that challenge the boundaries of technology and what it means to be human.
Read More & Download
